Prostatitis is the most common urological pathology characterized by an inflammatory process in the prostate. According to statistics, it occurs in almost 40% of men in the main risk group - patients aged 30–45 years. Almost every third visit to the urologist is associated with this condition.
Important!
The information in this article should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. You should always consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
The appearance of pathologies is often facilitated by a decrease in immunity, hypothermia, the presence of bad habits and a sedentary lifestyle, lack of regular sexual activity, sexual infections. Prostatitis can take a long time to treat, especially in the later stages of development. The sooner a man seeks medical help, the greater the chance of a successful recovery. Without timely therapy, the risk of serious consequences increases, including infertility, problems with sexual function and urination.
In the article we will talk about the mechanisms of the development of the disease, symptoms and causes, as well as modern methods of treatment.
What is the prostate
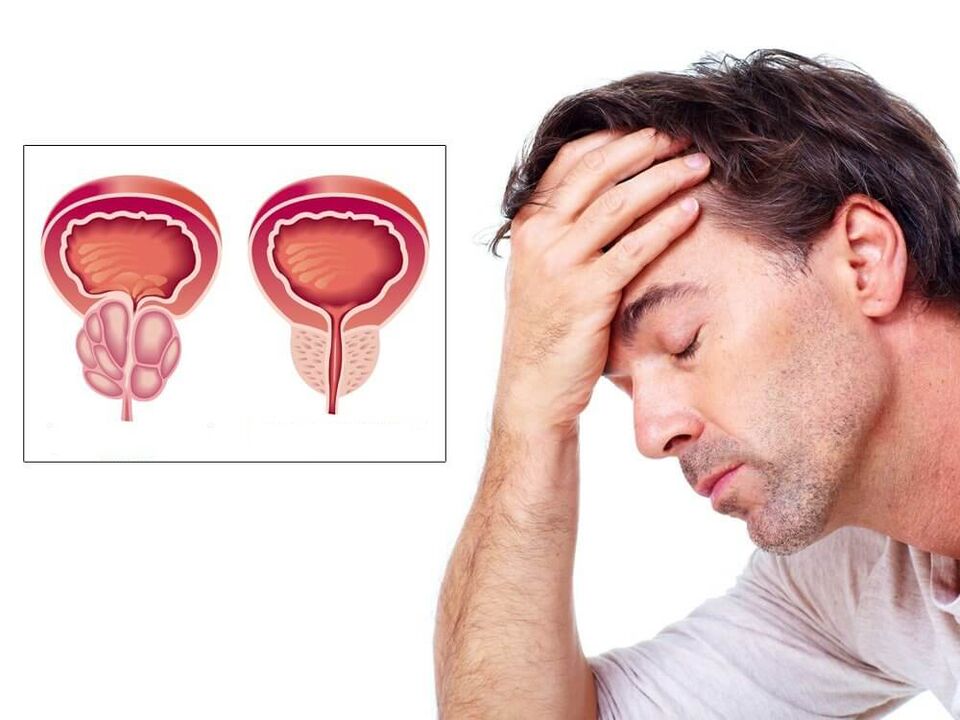
The prostate (or prostate gland) is an unpaired male organ responsible for producing secretions to maintain sperm activity. The organ is located under the bladder and surrounds the urethra. It is small - about the size of a walnut, but extremely important for men's health.
The prostate supports the production of sperm, ensures their movement and ejaculation, is involved in the development of sexual desire and the onset of orgasm, influences the activity of the testicles and the synthesis of androgens (male sex hormones).
All pathological processes in the prostate affect the composition of the prostatic secretion. As a result, the quality of sperm deteriorates and their ability to fertilize decreases. It also increases the risk of urinary tract infections because the prostate normally prevents bacteria from entering the urethra.
Unfortunately, diseases that require treatment of the prostate are quite common. Usually we talk about different tumor and hormonal processes. Prostatitis is considered one of the most common pathologies of the organ, since it has a different pathogenesis.
symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of prostate inflammation can vary depending on the form of the disease a man is diagnosed with. Regardless of the form, comprehensive treatment is chosen to eliminate the existing symptoms.
There are 3 groups of symptoms characteristic of prostatitis:
- pain syndrome. Pain in prostatitis can be different both in intensity and in localization. Sometimes the pain syndrome spreads to the lower abdomen, scrotum, perineum, anus and lower back. The more inflammation develops, the more pain worries the patient. The pain may become more intense during or after sexual activity or urination.
- Dysuric Syndrome. Due to the enlargement of the prostate, there is increased pressure on the ureters, which leads to a gradual decrease in its lumen. The patient has trouble urinating while feeling full bladder after going to the toilet.
- Sexual Deviations. In some cases, a man can often experience painful spontaneous erections or a complete lack of sexual arousal. With prostatitis, orgasmic sensations often fade and intercourse itself becomes short, or erection may disappear completely during intercourse.
One of the first signs of prostatitis in a man is frequent urination and discomfort in the groin area. There is a burning sensation in the urethra, which worsens when going to the toilet. There is general fatigue, decreased potency, accelerated or painful ejaculation. However, the disease is not always characterized by the appearance of corresponding symptoms. There are forms of prostatitis that are asymptomatic in the early stages. This means that diagnosing the pathology in such cases will be difficult.
causes
Often the disease occurs against the background of a decrease in immunity with sexual infections or concomitant pathologies. A common cause of prostatitis is a bacterial infection, against which inflammation of the tissues of the prostate begins.
There are many risk factors for the development of pathology, we will highlight the main ones:
- hypothermia. Hypothermia causes severe stress in the body, which can weaken the immune system. As a result, the pathogenic microflora begins to actively multiply, which leads to an inflammatory process.
- inactive lifestyle. Sedentary work and lack of physical activity negatively affect blood flow to the pelvic organs. This leads to congestion and inflammation.
- overweight. As a rule, obese patients lead an inactive lifestyle, which leads to impaired blood circulation in the internal organs. Stagnant processes and inflammation develop in the tissues of the prostate. For this reason, normalizing weight is considered one of the most important ways to prevent prostate disease.
- The presence of chronic diseases. A chronic focus of infection in the body increases the risk of prostate inflammation.
- Chronic constipation. The retention of feces in the intestine leads to pressure on the prostate, which causes circulatory disorders. In addition, constipation often contributes to the multiplication of pathogens.
- organ injury. In case of a traumatic lesion of the prostate or pelvic organs, blood circulation worsens, local immunity decreases. This increases the risk of developing prostatitis.
- Features of sexual activity. An overly active sex life or prolonged abstinence can also cause the onset of the disease.
In addition, any condition that weakens the immune system can contribute to the development of the disease. We are talking about constant stress, lack of sleep, overwork.
types of diseases
Often the symptoms of the pathology depend on its type and nature of the course. There are several types of prostatitis, each of which has its own characteristics:
- Bacterial. The most common type of disease that occurs as a result of bacterial infection and a decrease in immunity. There are acute and chronic forms of pathology. As a rule, a man is concerned about pain and discomfort in the perineum, disturbances in urination, deterioration in general well-being and fever. In severe cases, the presence of blood or pus in the urine is noted. However, these symptoms are more typical of the acute stage and relapses of the disease. With chronic prostatitis, symptoms may be "blurred" or not appear at all.
- abacterial. In this case, the disease is inflammatory rather than non-inflammatory in nature and is often referred to as chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS). With this form of prostatitis, destructive changes in the muscle tissue of the gland are observed. The causative agents are autoimmune diseases, abnormalities in the development of the organ, chronic cystitis.
- stagnates. This condition develops against the background of chronic prostatitis and is associated with impaired microcirculation and blood flow to the pelvic organs. In addition, the pathology can be manifested by a long absence from sexual intercourse, as this provokes stagnation of secretions in the prostate. Most often, patients with this form of the disease experience erectile dysfunction, urinary problems and groin discomfort.
- calculating. The development of this form of prostatitis contributes to the appearance of stones (stones) in the tissues of the prostate. As a rule, the disease occurs in patients older than 55-60 years. The causes of the pathology are improper treatment of chronic prostatitis or urolithiasis. The characteristic symptoms of such prostatitis in men include impaired urination, weakening of the erection and the appearance of blood in the urine.
- purulent. A dangerous consequence of improper treatment of acute prostatitis can be a purulent form of the disease. In this case, acute pain syndrome develops, affecting the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe perineum and groin. A man has a sharp rise in temperature, severe problems with urination and the presence of purulent inclusions in the urine. Purulent prostatitis is considered the most dangerous, since if left untreated it can cause an abscess and lead to death.
diagnosis of prostatitis
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by a urologist - it is worth making an appointment with him if characteristic symptoms appear. During the first consultation, the specialist takes the medical history, asks about existing symptoms and carries out a rectal examination of the prostate. After that, a number of additional examinations necessary to diagnose the existing type of prostatitis and prescribe competent treatment are prescribed.
The survey includes:
- Ultrasound (TRUS) of the pelvic organs.
- Clinical blood test.
- General urinalysis.
- Microscopic analysis of the prostate secretion.
- A smear from the urethra and bacterial sowing give the secret of the presence of sexually transmitted infections.
If necessary, the patient can be referred for additional examinations: spermiogram, CT (or MRI) of the pelvic organs.
Important!
The information in this article should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. You should always consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
treatment methods
Inadequate treatment of prostatitis can lead to serious health problems. Patients are often diagnosed with complications such as cystitis, vesiculitis, pyelonephritis, infertility and erectile dysfunction. Therefore, the right choice of therapy is extremely important.
Prostate inflammation is usually treated with a holistic approach consisting of medication and supportive care. In difficult cases, the patient is operated on.
As part of drug therapy, antibiotics are prescribed to stop the inflammatory process. If the disease is of an infectious-bacterial nature, antibacterial treatment is additionally carried out.
Drugs are also used as part of drug therapy to eliminate existing symptoms. It may be:
- Painkiller.
- antispasmodics and muscle relaxants.
- diuretics.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Drugs to normalize prostate function.
- Preparations to restore erection.
It is imperative to follow a number of recommendations:
- Drink enough water throughout the day (1. 5-2 liters).
- Diet, exclusion of spicy, fatty and salty foods.
- exclusion of alcohol.
Sometimes medicinal herbal preparations are used to relieve inflammation, which have a bactericidal effect. However, taking infusions and decoctions is only permitted after consultation with the urologist. Remember that folk remedies are not a panacea for the disease and will only help with the symptoms, but will not eliminate the cause.
An important part of the treatment is the prostate massage. It is carried out in the absence of contraindications. The essence of this procedure is to remove the accumulated inflammatory secret from the body. Thanks to this, it is possible to improve tissue blood flow, remove congestion, stimulate local immunity and restore patency of the secretory ducts.
Another popular method is the use of physical therapy. In the 21st century, it is difficult to imagine high-quality modern treatment of chronic prostatitis without the use of complex physiotherapy. With its help, it is possible to restore blood flow to the pelvic organs, enhance the effect of drugs, and get rid of congestion. Ultrasound, laser, thermal or electromagnetic effects are used as part of the therapy.
With a long course of the inflammatory process and a decrease in immunity, the patient is prescribed immunotherapy. It includes taking immunomodulators and multivitamin complexes to improve the protective functions of the body and general well-being.
Sometimes conservative treatment of prostatitis does not bring the desired results, so the patient needs surgery.
Of course, surgery requires a long recovery and often provokes a number of complications, including infertility. Therefore, it is not performed on young men of childbearing age.
Symptoms and treatment of acute prostatitis
Acute prostatitis is characterized by rapid onset and rapid development. It is worth noting that it happens quite rarely - in about 5% of cases.
The inflammatory process in the prostate develops progressively, so several stages of the acute form can be distinguished:
- catarrhal. The inflammatory process affects individual lobes of the organ, affects the structure of the mucous membranes and submucosal layer. As a result, congestion occurs in the follicles of the gland.
- follicle. There is focal suppuration of the affected lobes.
- parenchyma. There is a multiple lesion of the organ, almost all tissues are involved in the inflammatory process. An abscess is formed, which can open with the release of purulent contents into the bladder, urethra or rectum.
Among the symptoms of acute prostatitis: severe pain, fever, chills, profuse sweating, weakness. This condition can be caused by various microorganisms. The most common cause is Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter.
Treatment of the pathology should be started immediately after the appearance of the first symptoms. As a rule, complications and health consequences can be avoided in such cases. The patient is given a combination of antibiotics that are effective against the pathogen present. In this case, the effect of therapy is observed after 2-3 days. In a man, almost all symptoms disappear, the process of urination normalizes, and signs of infection disappear.
In the absence of the necessary therapy, urinary tract obstruction and abscess may develop. Such conditions require urgent hospitalization and often surgical intervention.
Symptoms and treatment of chronic prostatitis
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by sluggish development. Symptoms are intermittent or absent, which is why many men ignore their presence for years and do not seek medical attention.
At the same time, at the very beginning of the development of pathology, patients note an increase in sexual desire and spontaneous erections. But at the same time, such signs of chronic prostatitis appear in the form of a decrease in the duration of sexual intercourse and painful ejaculation. As the disease progresses, symptoms become less pronounced, but deterioration in well-being increases. Many complain of a lack of morning erection, reduced libido and increased sweating in the groin.
During an exacerbation of prostatitis in a man, there is pain in the genital area, impaired urination, and fever. However, other pathological symptoms may be absent, which often complicates the diagnosis.
An accurate diagnosis requires a comprehensive examination that includes a medical history, a rectal examination of the prostate, and a series of laboratory tests. In some cases, additional instrumental methods are used.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis in the chronic form lasts from 3-4 weeks to 6-12 months. Of paramount importance is the elimination of the causes of the inflammatory process in the prostate. Otherwise, the recurrent nature of the pathology cannot be ruled out.
Precautions
For the prevention of prostatitis in men, lifestyle correction and abandonment of bad habits are recommended. This is due to the fact that while maintaining the factors conducive to the development of the disease, recurrence is possible. A key role in prevention is played by proper nutrition, good sleep and physical activity, as well as a regular sex life.
In addition, in order not to encounter inflammation of the prostate, urologists advise adhering to the following recommendations:
- Avoid hypothermia.
- If you are sitting, take regular short breaks and light workouts.
- Incorporate exercise and walking into your routine.
- Normalize the diet and get rid of constipation (it is better to consult a specialist about the problem).
- Have a regular sex life with a steady partner.
- From the age of 40, annual check-ups by a urologist.
And, of course, you should remember that if you have any signs of prostatitis, you should immediately consult a doctor. This is the only way to avoid dangerous health consequences.